SODIUM COCOYL GLUTAMATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
68187-32-6
(Monosodium)
68187-30-4 (Disodium)
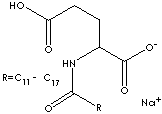
269-085-1 (Disodium)
3402.11
TOXICITY
Sodium N-Cocoyl L-Glutamate;
CLASSIFICATION
SURFACTANTS /
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
8 - 9 (5% Sol.)
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
Anionic surfactant is the widely used type of surface active agent for laundry detergents, liquid cleaners and shampoos due to excellent cleaning properties particularly effective at oily soil cleaning and oil/clay soil suspension. Anionic surfactants are deactivated in many hard water. To prevent deactivation, builders should be dosed. Anionic surfactant is used as a emulsifier in cosmetics, tooth paste, cream, shampoo, and acrylic binder. Common soap is an anionic surfactant. Carboxylate, sulfate, sulfonate and phosphate are the polar groups in anionic surfactants. Anionic surfactants include alkyl benzene sulfonate, fatty acid salts, sodium lauryl sulfate, alkyl sulfate salts, sodium lauryl ether sulfate, alpha-olefin sulfonates, phosphate esters, sulphosuccinates, alkyl phenol ether sulfates, and isethionates.
Anionic co-surfactant for mild, biodegradable and high foaming properties to provide gentle cleansing and soft skin feel.
APPEARANCE
pH
8 - 9 (5% Sol.)
FREE FATTY ACID
2.0% max
Carbon distribution: >, C8/10 13 (%) + C12 45 - 55(%) + C14 25(%) + C16 15(%) + C18, < 12(%)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FATTY ACID
Commercial fats produced by organic processes in plants are palm, coconut, palm kernel, sunflower, soybean, and other oils. Their main components are triolein and triglyceryl esters of stearic (C18), palmitic (C16), myristic(C14), lauric (C12), oleic (C18:1), and other fatty acids. Tallow is a refined hard fat extracted from fatty deposits of animals, especially from suet (fatty tissues around the kidneys of cattle and sheep). The molecules of most natural fatty acids have an even number of carbon chains due to the linkage together by ester units. Analogous compounds of odd numbers carbon chain fatty acids can be made synthetically. All fats are insoluble in water and have lighter weight than water. Industrial fats can be sub-classified as fat, grease or oil depending on melting point. Fats that are liquid at room temperature are referred to oil. Grease has a higher initial viscosity than oil. It is used as a lubricant. The organic processes to convert fats to fatty acids (or esters) and glycerol is called oleochemistry. Fatty acids and glycerol are produced by hydrolysis (addition reaction of water molecule with cleavage of parent molecules) of the triglycerides. Fatty esters are produced by esterification reaction. Coconut or palm oils are better source to get saturated fatty acids than sunflower, soybean or rapeseed oils which have more unsaturated fatty acids composition of triglycerides. Tall oil is a source of low boiling point fatty acids. Generally, commercial coconut fatty acid has carbon chain composition of; C10 (5% max) + C12 (45 - 55%) + C14 (20 - 25%) + C16 (10 - 15 %) + C18 (10 - 15% max, including unsaturated fatty acids). Fats are used to make soap, food products, cosmetics, and candles, and lubricants. They are wisely used in producing synthetic surfactants.